App Usage Flow
Overview¶
The application has been developed by the app owner. Therefore, how to use it depends on its own API.
However, there are some specificities about the connection depending on the Cosmian Enclave configuration namely the scenarios chosen by the app owner.
The TLS connection is specific to each scenario:
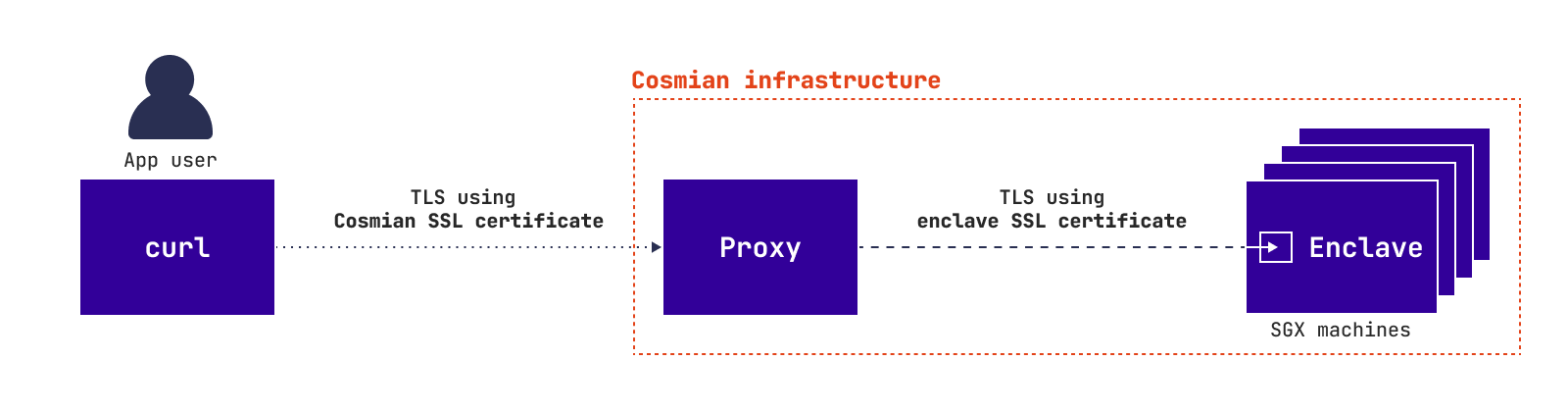
Zero trust approach¶
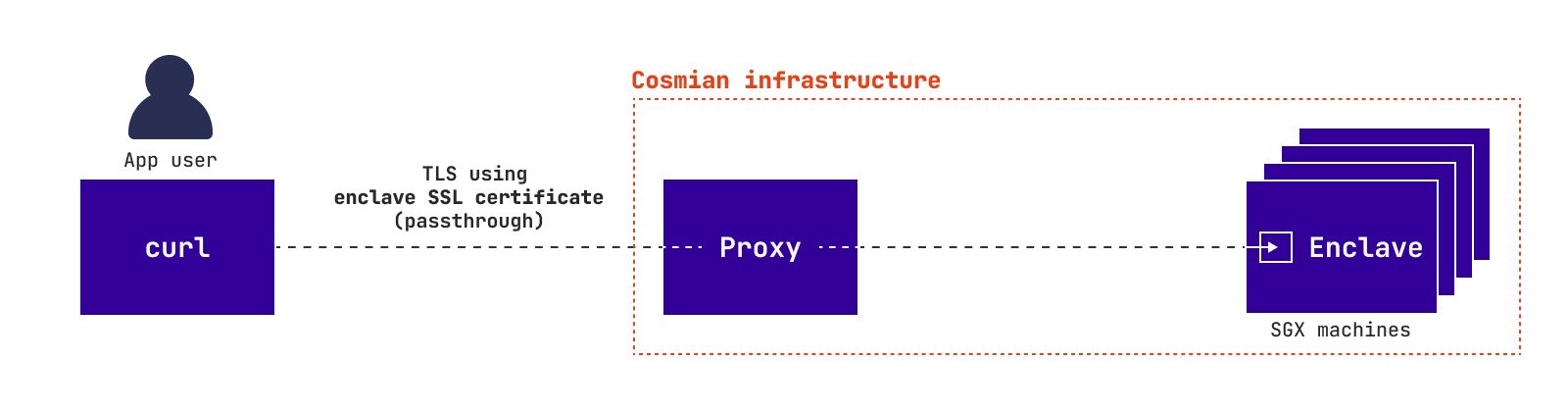
App owner trust approach¶
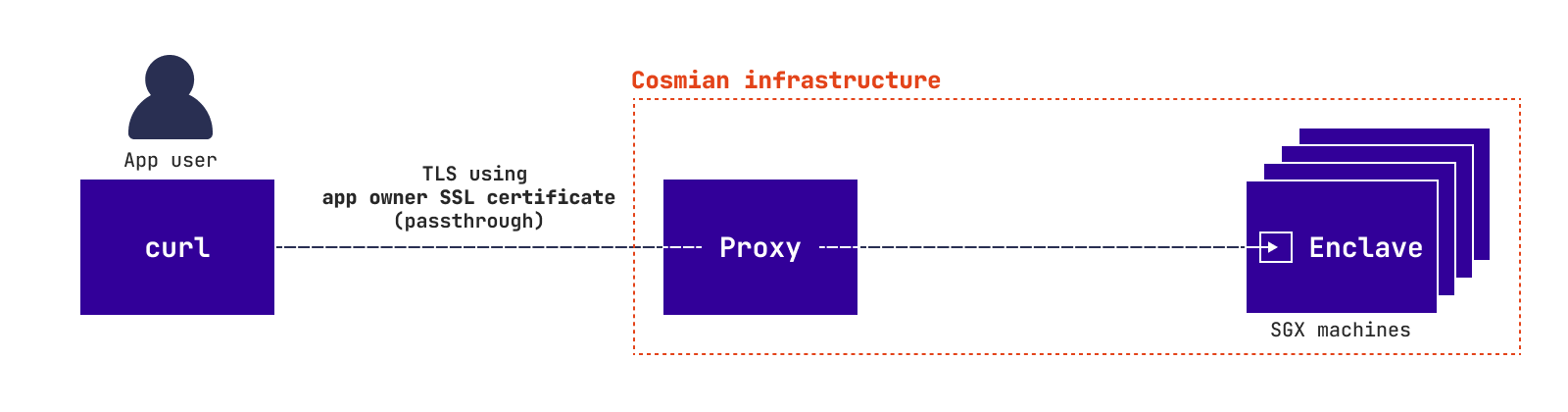
Application deployed using --untrusted-ssl¶
In all scenarios but Zero trust approach the user trusts the app owner. Therefore, the user does not need to verify the Cosmian Enclave app. So, the user can use the app as if it is running inside a classic cloud.
In Zero trust approach the user has to verify the Cosmian Enclave app and the SSL certificate before querying the app. The following diagram explains how it works:
Usage process¶
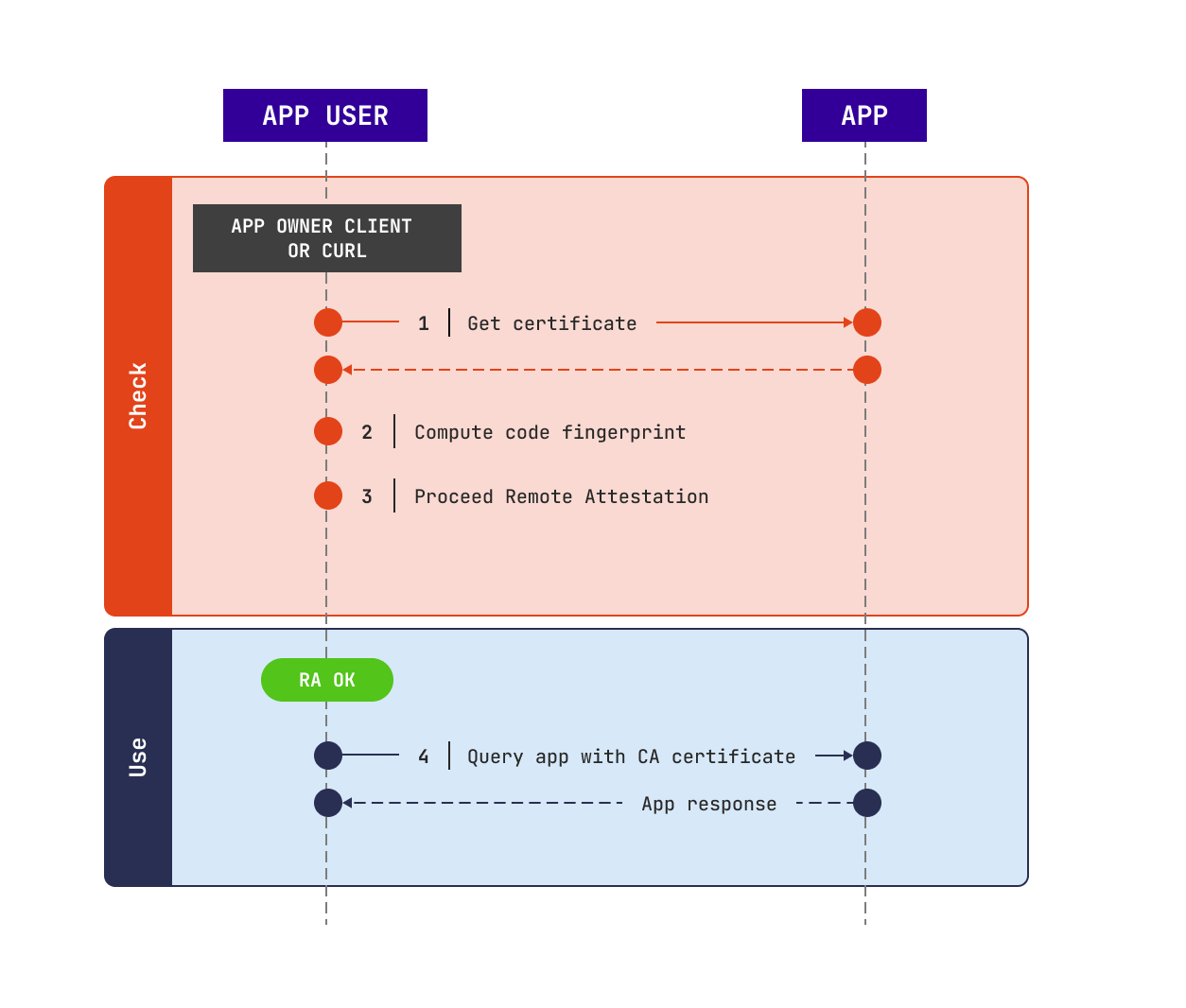
Cosmian Enclave instance verification¶
The app user should verify the Cosmian Enclave app, that is to say:
- check that the code is running inside an enclave
- check that this enclave belongs to Cosmian
- check that the code is exactly the same as provided by the app owner
If one of those fails, the app owner must stop querying the application.
Otherwise, the app user should use this certificate to proceed the next queries.
For more details about this step, read security.
This verification can be done using: mse cloud verify:
- code fingerprint can be checked against a fingerprint provided by the app owner, with
--fingerprint FINGERPRINT - code fingerprint can be computed by the user on their own, with the options
--contextand--code. The context file and the plain text code must be provided by the app owner to the user by their own means. See the context subcommand - the verification of the code fingerprint is omitted if you don’t provide the previous arguments
$ mse cloud verify my_app.cosmian.io
Checking your app...
Code fingerprint check skipped!
Verification: success
The verified certificate has been saved at: ./cert.pem
Working with the web browser¶
As a Cosmian Enclave app security is based on a new SSL standard called RATLS, your browser will pop up a security warning when accessing your micro-service for the first time.
After downloading and verifying your web service RATLS certificate as shown previously, you can add it to your web browser certificates store. For Chrome for example, run:
sudo apt install libnss3-tools
certutil -d ~/.pki/nssdb/ -A -i ratls.pem -n "<APP_ID>" -t C,,
# Read: https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/Network_Security_Services for more details
# Or: https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/User:Grawity/Adding_a_trusted_CA_certificate
Then, you can access your microservice through your web browser. If the warning message occurs again: it means that the microservice has been updated, and then you should download the new certificate, verify it again and then add it you your SSL store.
When accessing to your microservice, you can verify than the connection is managed by RATLS by checking the certificate on the left of the url field.
Note than the RATLS certificate is not compatible with Firefox policies and won’t work.
Warning
Do not click on the button “Accept the risk”: do always proceed the verification and add the certificate as described previously